Monitoring your validator with Grafana and Prometheus
1. Install Prometheus and Node Exporter
sudo apt-get install -y prometheus prometheus-node-exporter2. Install Grafana
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common wget
sudo wget -q -O /usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key https://apt.grafana.com/gpg.keyecho "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/grafana.key] https://apt.grafana.com stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/grafana.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y grafana3. Enable services so they start automatically
sudo systemctl enable grafana-server prometheus prometheus-node-exporter4. Create the prometheus.yml config file
sudo rm /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
sudo nano /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml5. Setup prometheus for your execution client
6. Create a SSH Tunnel to Grafana
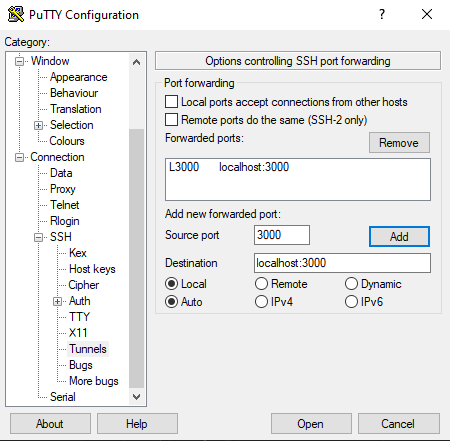
7. Setup Grafana Dashboards
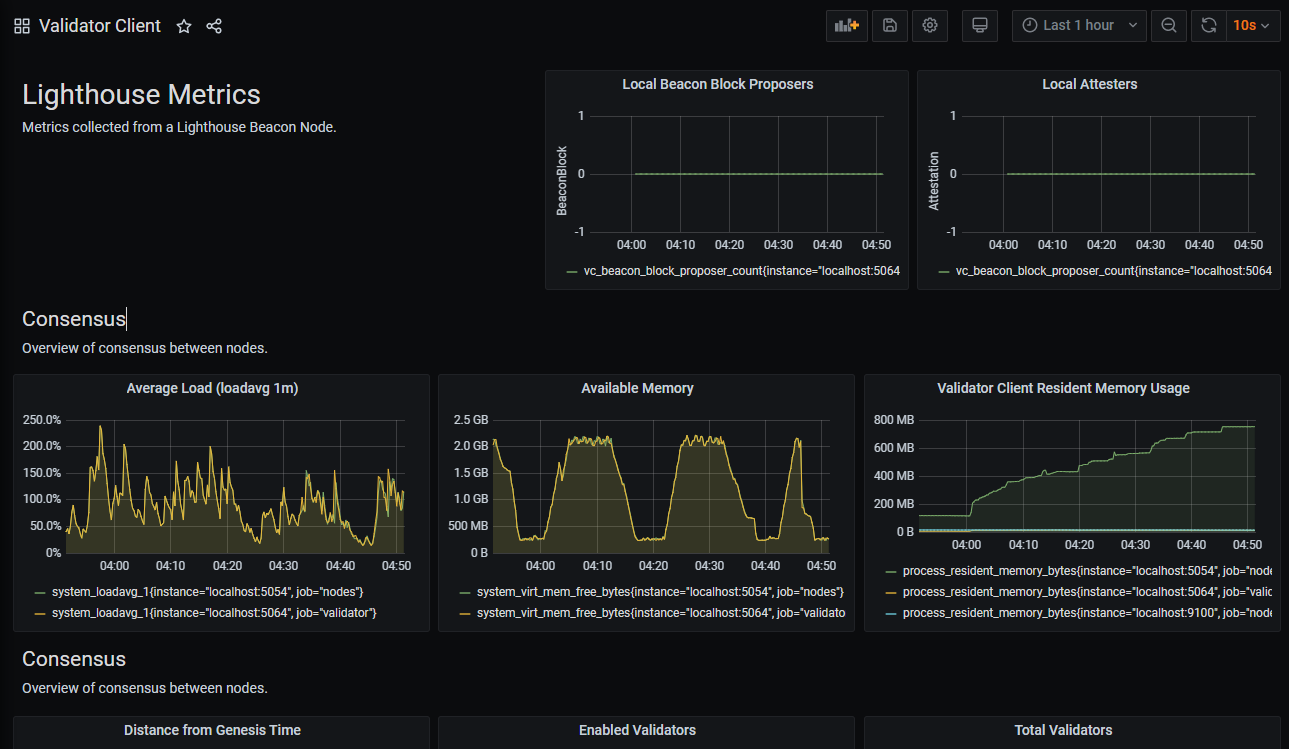
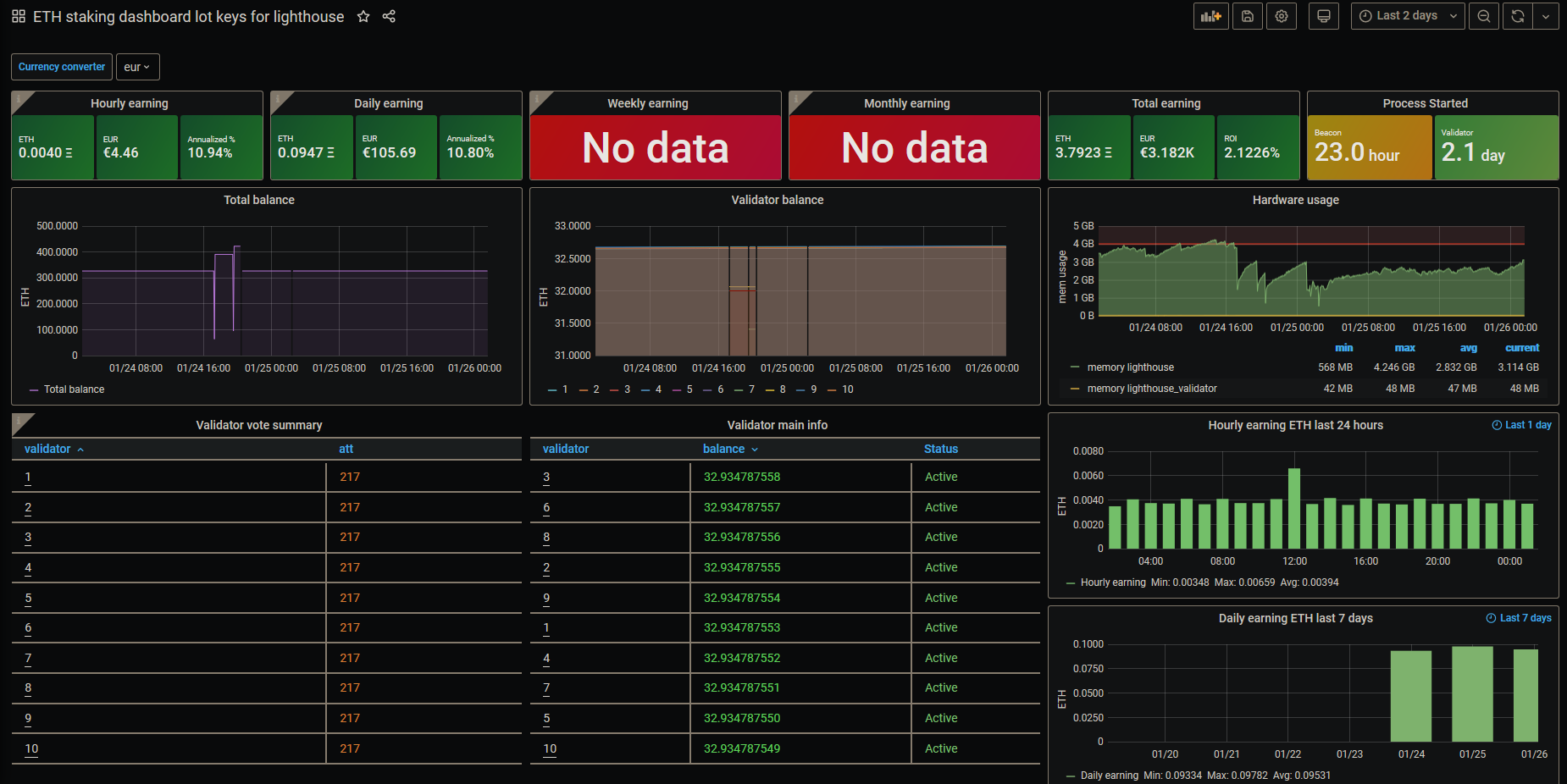
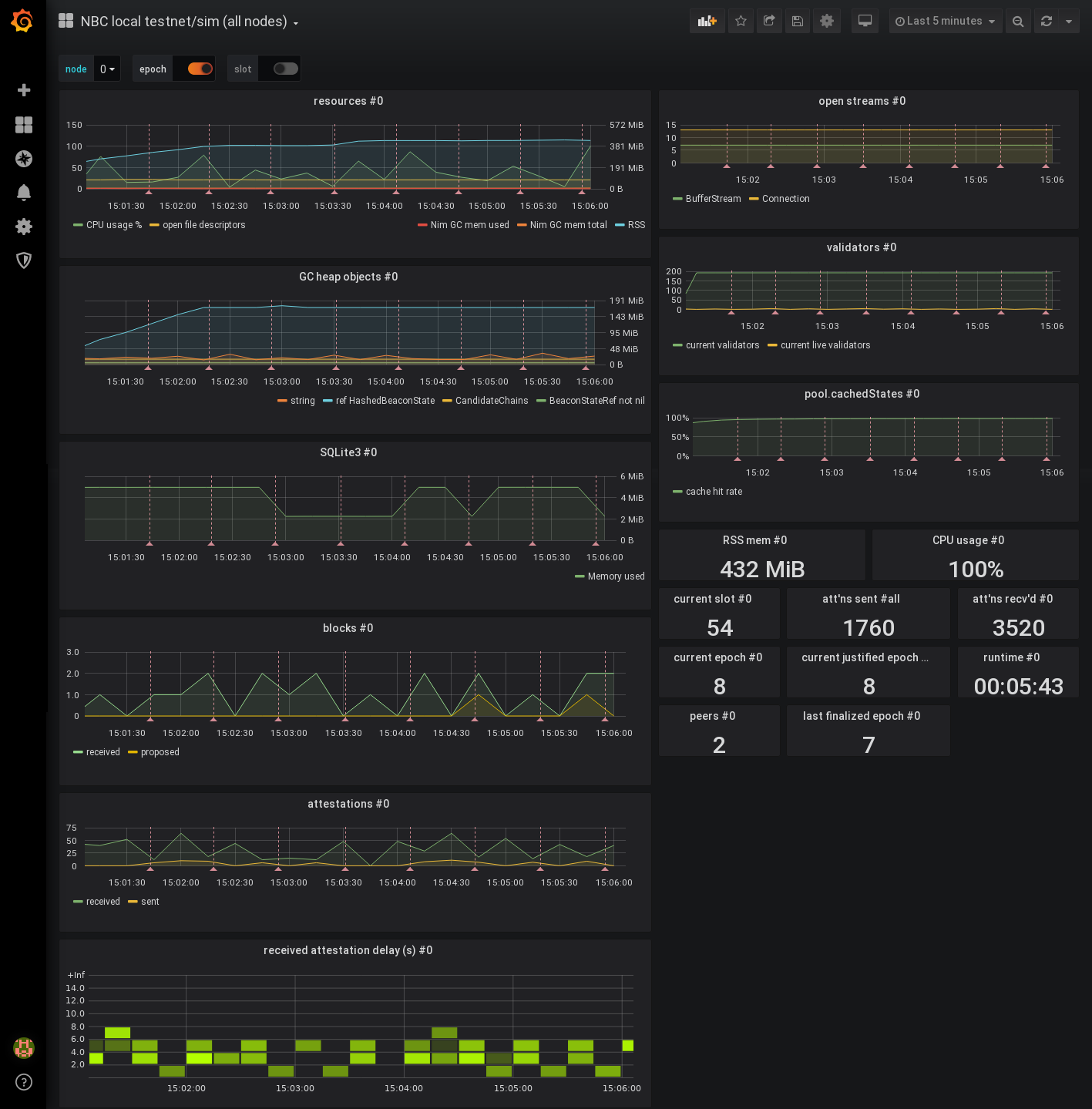
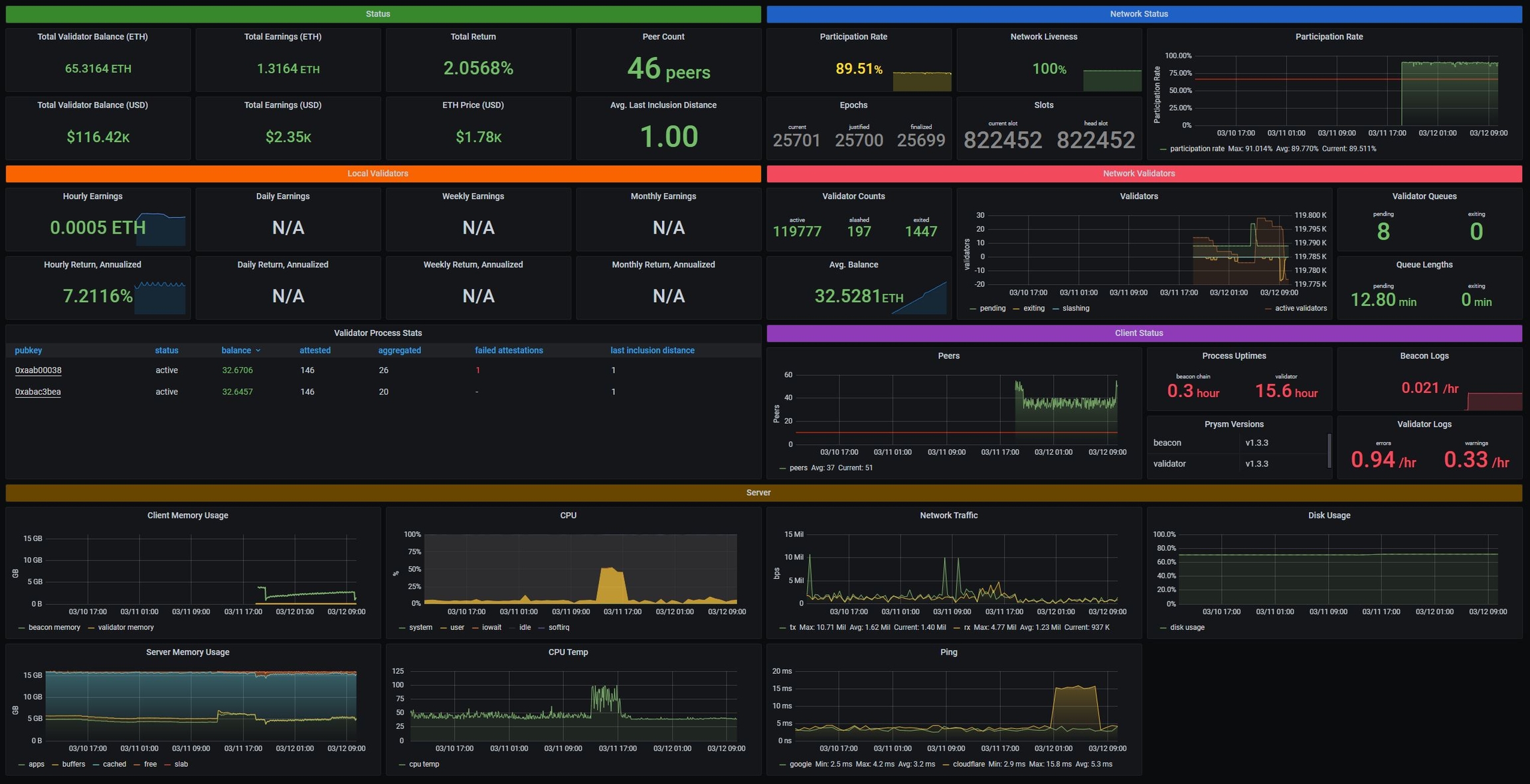
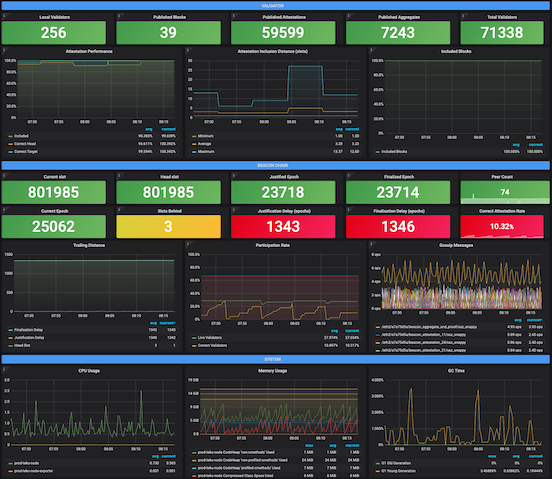
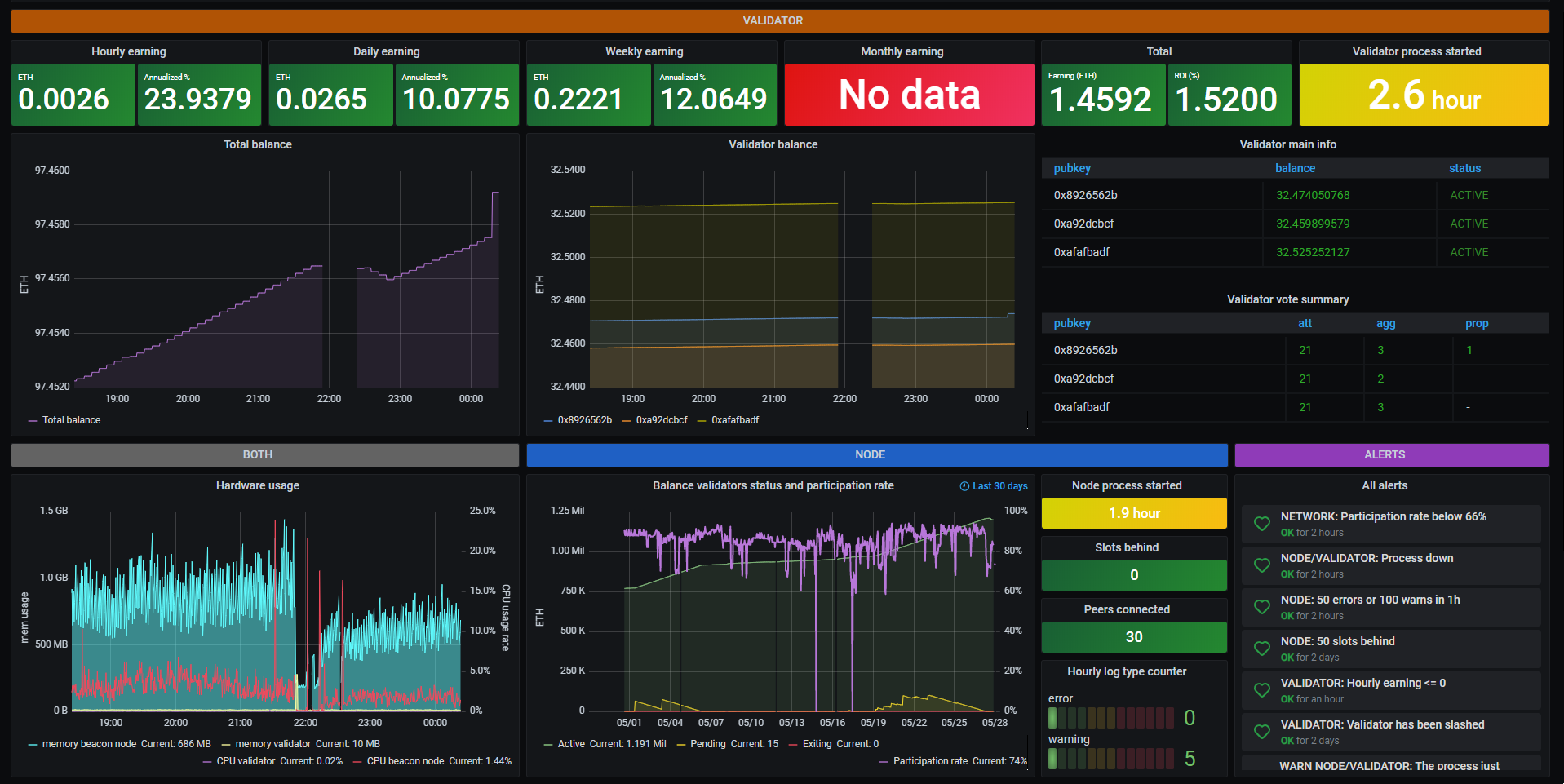
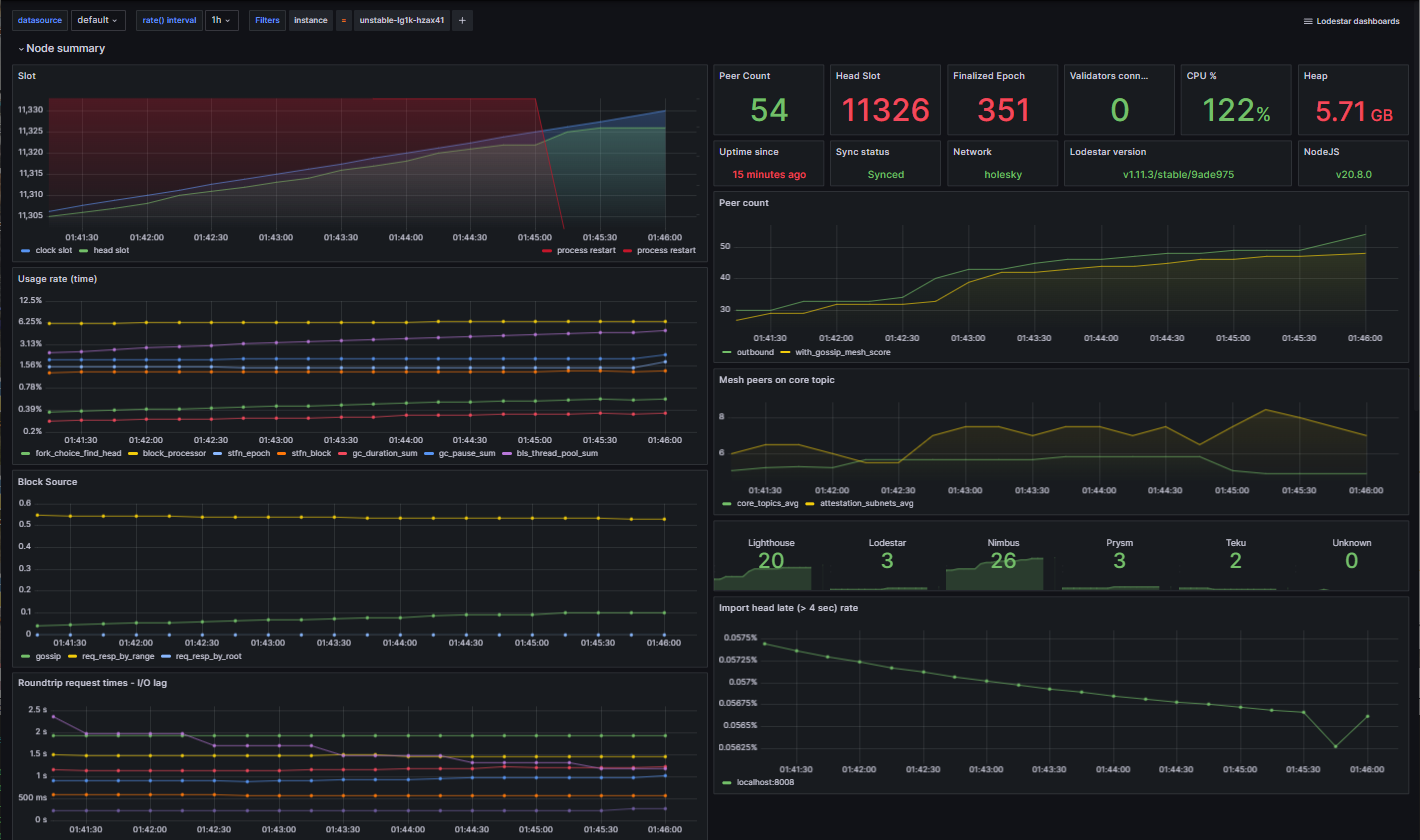
Example of Grafana Dashboards for each consensus client.

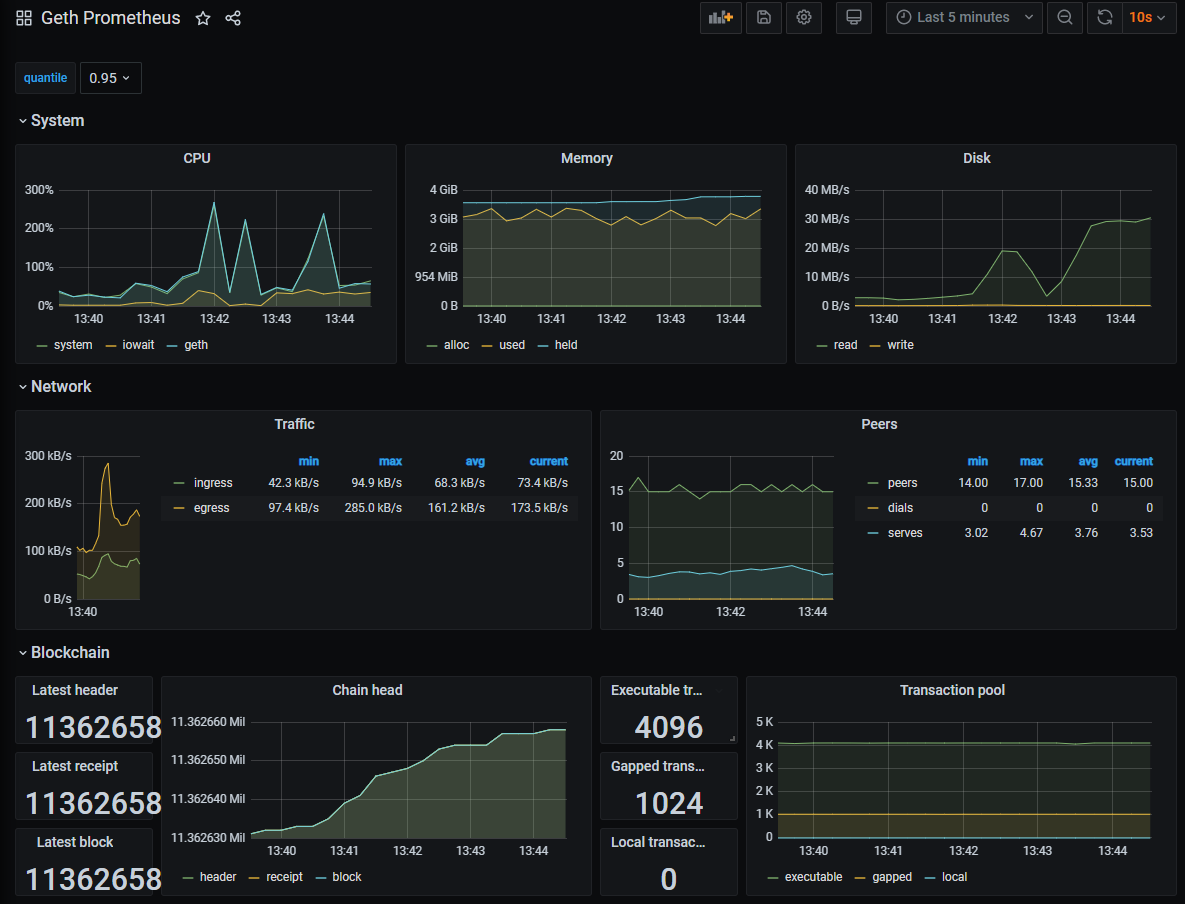
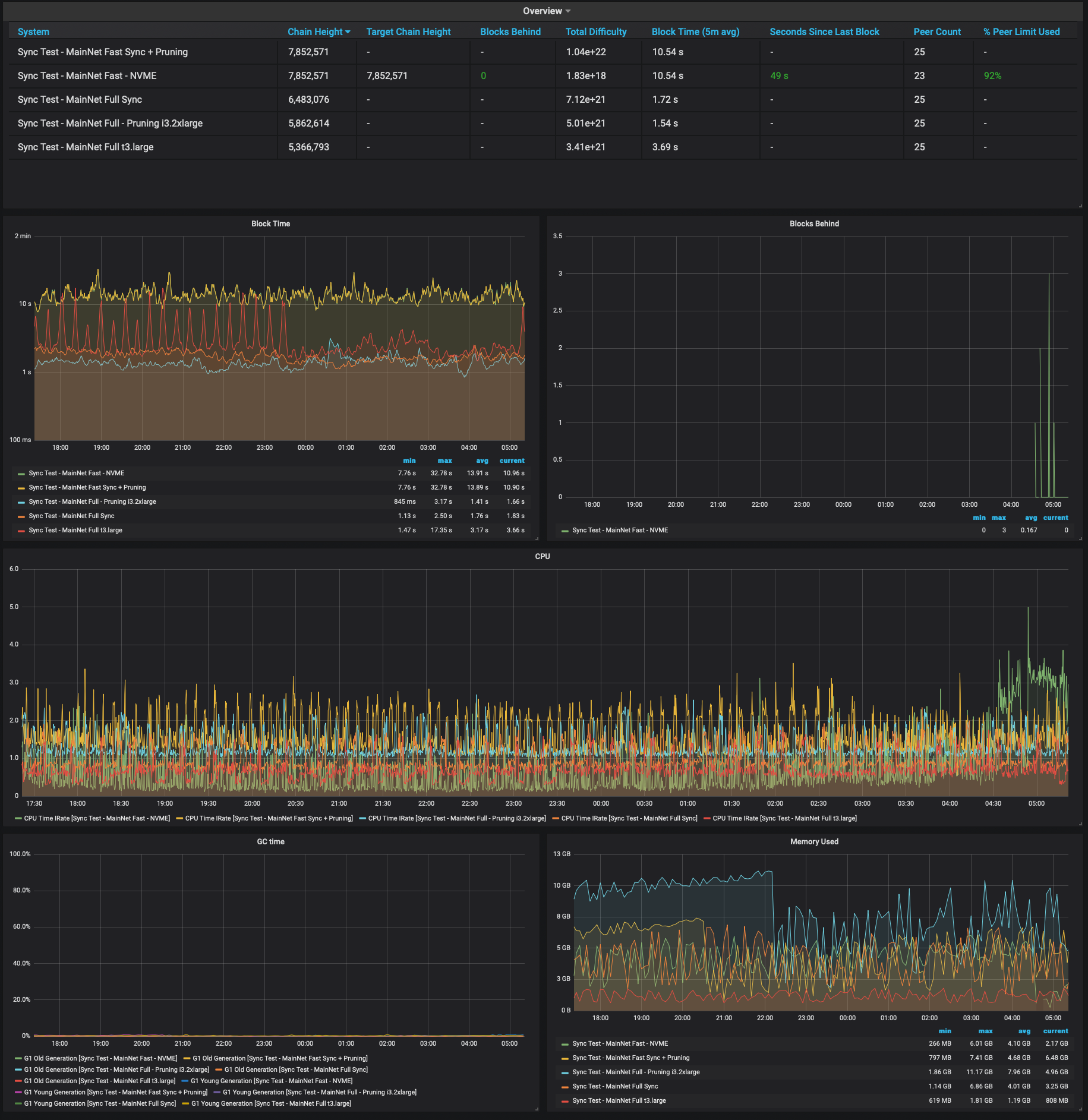
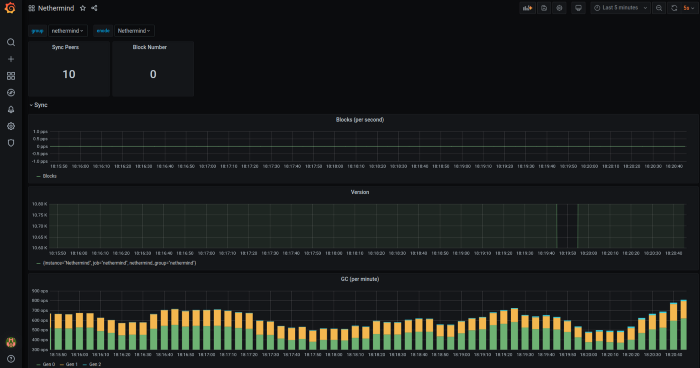
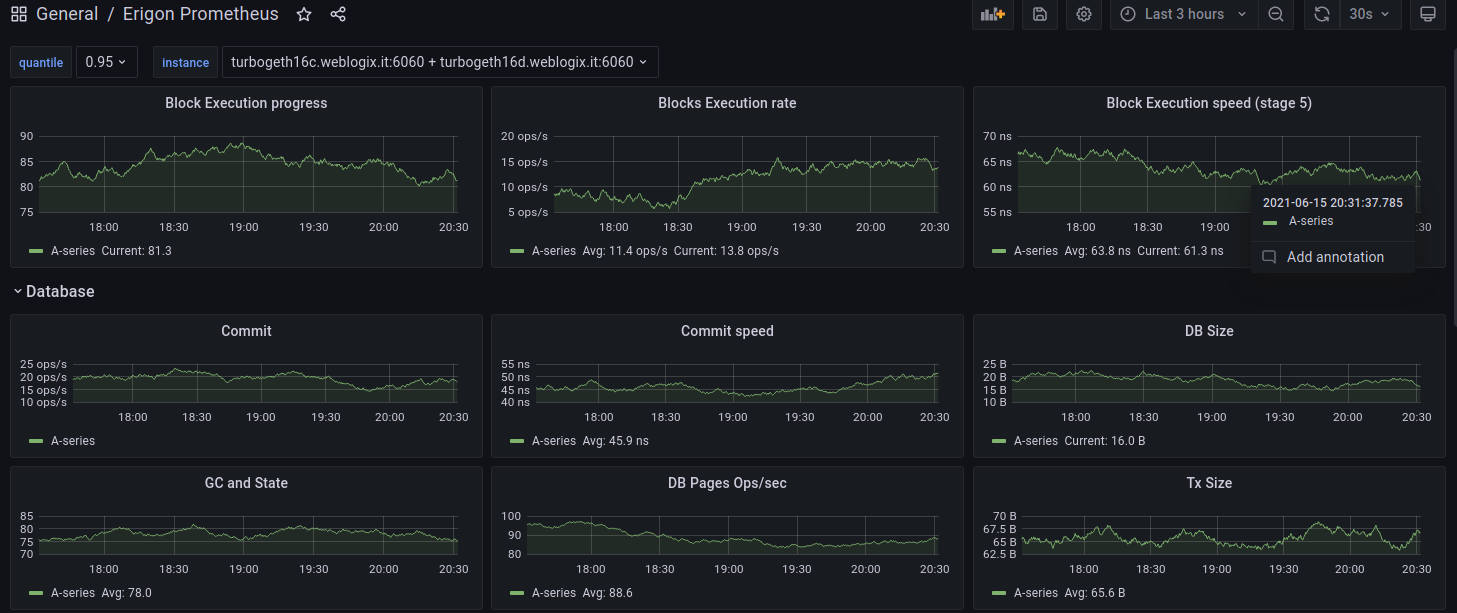
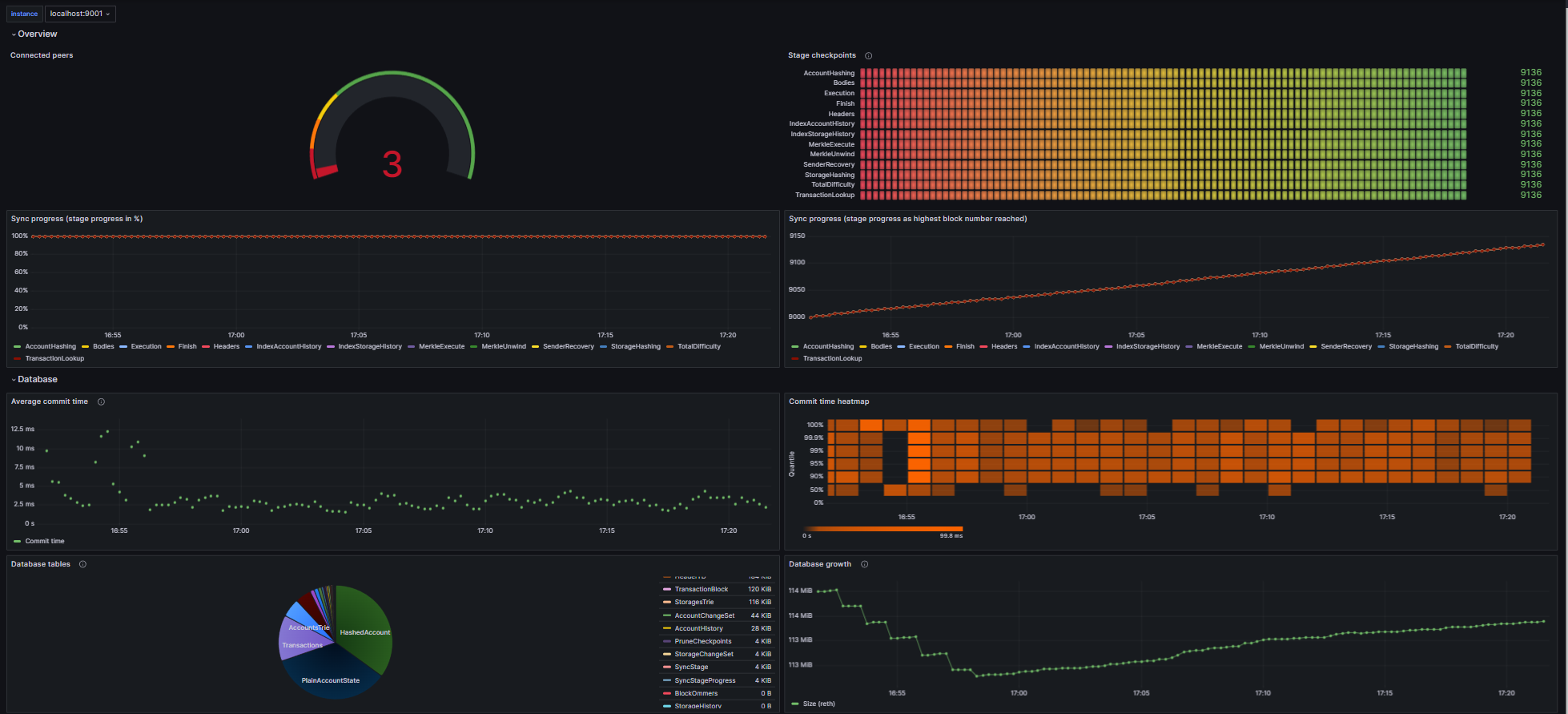
Example of Grafana Dashboards for each execution client.
Example of Node-Exporter Dashboard