Guide | Ethereum Staking on Zhejiang Testnet
Become a validator, start staking and help secure Ethereum, a proof-of-stake blockchain. Anyone with 32 ETH can join.
Your Mission - #TestingTheWithdrawalsShanghai
Overview: To participate in the public testnet known as Zhejiang, the first public effort to test Ethereum’s upgrade to enabling validator withdrawals with a hardfork called "Shanghai-Capella" or also known as EIP 4855.
Goals: To test your staking setups, practice voluntary exits and validator withdrawals.
Staked ETH: With the new ability to withdraw staked ETH since beacon chain genesis on December 1 2020, this upgrade to Ethereum POS will add flexibility and attract the next wave of stakers and innovation.
Client Diversity: Within the Ethereum network of nodes, you want to improve Ethereum's client diversity by choosing a minority execution and consensus client combination.
Timeline: Assuming this testnet is thoroughly tested, mainnet Ethereum could be upgraded sometime in March 2023.
As of early February 2023, Besu is the most minority execution client with 6.8% of nodes. Lodestar is by far the most minority consensus client with 0.29% representation.

How Staking on Ethereum Works
Acquire some hardware (laptop, desktop, server) or rent a VPS (cloud server): You need to run a node to stake.
Sync an execution layer client
Sync a consensus layer client
Generate your validator keys and import them into your validator client
Monitor and maintain your node
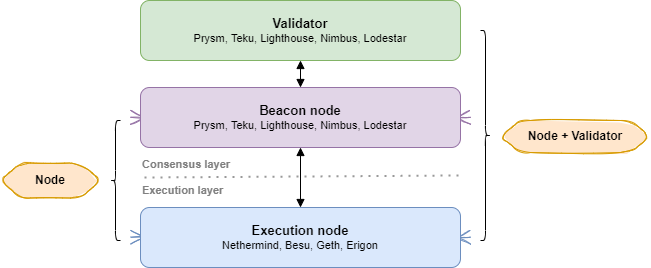
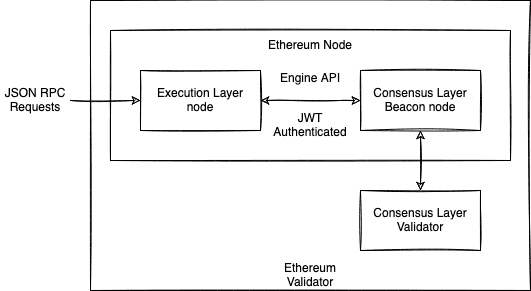
A Ethereum node consists of the Execution Layer + Consensus Layer.
A Ethereum Staking node is the previous plus a Validator client.
Prerequisites
This guide was written for aspiring Ethereum stakers who have basic familiarity with command line tools and it was tested against Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS client. You’ll want a dedicated cloud VPS or local desktop/server/laptop running a clean install of Ubuntu preferably.
If using a VPS or remote server, install and start the SSH client for your operating system:
Windows: PuTTY
MacOS and Linux: from the Terminal, use the native command:
How to Run Commands
Commands are to be run in a terminal window or ssh terminal.
Commands preceded by
sudowill prompt for your password at first, and periodically afterwards.
Minimum Hardware Requirements
Operating system: 64-bit Linux (i.e. Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Server or Desktop)
Processor: Dual core CPU, Intel Core i5–760 or AMD FX-8100 or better
Memory: 16GB RAM
Storage: 40GB SSD
Recommended Hardware Requirements
Once done with testnet staking, this hardware configuration would be suitable for a mainnet staking node.
Operating system: 64-bit Linux (i.e. Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Server or Desktop)
Processor: Intel i5 or AMD Ryzen 5 or better.
Memory: 32GB RAM
Storage: 2TB SSD or NVME
Network: 100 Mbit or faster connection with at least 2TB per month data plan
For examples of actual staking hardware builds, check out RocketPool’s hardware guide.

Pro Staking Tip: Highly recommend you begin with a brand new instance of an OS, VM, and/or machine. Avoid headaches by NOT reusing testnet keys, wallets, or databases for your validator.
How to participate with Zhejiang
Step 1. Install dependencies and updates
Install packages and update OS.
Reboot your machine to update installation.
Step 2. Configure Firewall
Initialize the firewall with Ethereum’s p2p ports and ssh.
Confirm the settings are in effect.
Example output:
For optimal connectivity, ensure Port Forwarding is setup for your router. Learn to port foward with guides found at https://portforward.com/how-to-port-forward
Step 3. Synchronize Time with Chrony
Install Chrony with the following.
Wait a few seconds, then verify that Chrony is syncing time.
Step 5. Setup Execution Layer Client
Setup your execution layer client, your choice of Nethermind, Erigon, Geth or Besu.
Only one execution layer client is required per node.
Hyperledger Besu is an open-source Ethereum client designed for demanding enterprise applications requiring secure, high-performance transaction processing in a private network. It's developed under the Apache 2.0 license and written in Java.
Nethermind is all about performance and flexibility. Built on .NET core, a widespread, enterprise-friendly platform, Nethermind makes integration with existing infrastructures simple, without losing sight of stability, reliability, data integrity, and security.
Erigon is an implementation of Ethereum innovating on the efficiency frontier, written in Go.
Geth - Go-ethereum (aka Geth) is an Ethereum client built in Go. It is one of the original and most popular Ethereum clients.
Install Nethermind
Install dependencies.
Review the latest release at https://github.com/NethermindEth/nethermind/releases
Run the following to automatically download the latest linux release, un-zip and cleanup.
Install the binaries.
Download the testnet configs.
Create a service user for the execution service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Generate the JWT secret, a file used by both the execution and consensus client, add read access privileges for the consensus client and setup ownership permissions
Create a systemd unit file to define your execution.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Install Besu
Install dependencies.
Build the binaries.
Verify Besu was properly built by checking the version.
Sample output of a compatible version.
besu/v23.1.0-dev-e18e407c/linux-x86_64/openjdk-java-17
2023-02-02 01:22:12.000+00:00 | main | INFO | Besu | Using jemalloc
Install the binaries.
Create a service user for the execution service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Generate the JWT secret, a file used by both the execution and consensus client, add read access privileges for the consensus client and setup ownership permissions
Create a systemd unit file to define your execution.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Install Erigon
Install Go dependencies
Verify Go is properly installed by checking the version and cleanup files.
Install build dependencies.
Build the binary.
Install the binary.
Create a service user for the execution service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Generate the JWT secret, a file used by both the execution and consensus client, add read access privileges for the consensus client and setup ownership permissions
Create a systemd unit file to define your execution.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Initialize database
Install Geth
Install Go dependencies
Verify Go is properly installed by checking the version and cleanup files.
Install build dependencies.
Build the binary.
Install the binary.
Create a service user for the execution service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Generate the JWT secret, a file used by both the execution and consensus client, add read access privileges for the consensus client and setup ownership permissions
Create a systemd unit file to define your execution.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Initialize database
Run the following to enable auto-start at boot time.
Finally, start your execution layer client and check it's status.
Press Ctrl + C to exit the status.
Step 6. Setup Consensus Layer Client
To strengthen Ethereum's resilience against potential attacks or consensus bugs, it's best practice to run a minority client in order to increase client diversity. Find the latest distribution of consensus clients here: https://clientdiversity.org
Set up your consensus layer client. Your choice of Lighthouse, Nimbus, Teku, Prysm or Lodestar.
Lodestar is a Typescript implementation by the Chainsafe.io team. In addition to the beacon chain client, the team is also working on 22 packages and libraries. Finally, the Lodestar team is leading the Ethereum space in light client research and development and has received funding from the EF and Moloch DAO for this purpose.
Lighthouse is an Ethereum client with a heavy focus on speed and security. The team behind it, Sigma Prime is an information security and software engineering firm who have funded Lighthouse along with the Ethereum Foundation, Consensys, and private individuals. Lighthouse is built in Rust and offered under an Apache 2.0 License.
Teku is a Java-based Ethereum 2.0 client designed & built to meet institutional needs and security requirements. Dedicated to building enterprise-ready clients and tools for interacting with the core Ethereum platform, Teku is Apache 2 licensed and written in Java, a language notable for its maturity & ubiquity.
Nimbus is a research project and a client implementation for Ethereum 2.0 designed to perform well on embedded systems and personal mobile devices, including older smartphones with resource-restricted hardware. The Nimbus team are from Status the company best known for their messaging app/wallet/Web3 browser by the same name. Nimbus (Apache 2) is written in Nim, a language with Python-like syntax that compiles to C.
Prysm is a Go implementation of Ethereum 2.0 protocol with a focus on usability, security, and reliability. Prysm is developed by Prysmatic Labs, a company with the sole focus on the development of their client. Prysm is written in Go and released under a GPL-3.0 license.
Install Lighthouse Consensus Client
Install rust dependency
When prompted, enter '1' to proceed with the default install.
Update your environment variables.
Install rust dependencies.
Build the binaries.
Verify lighthouse was built properly by checking the version number.
Install the binary.
Create a service user for the consensus service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Setup ownership permissions.
Create a systemd unit file to define your consensus.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Install Teku Consensus Client
Install Java 17 LTS.
Verify Java 17+ is installed.
Build the binaries.
Verify Teku was built properly by displaying the version.
Install the binaries.
Create a service user for the consensus service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Setup ownership permissions.
Create a systemd unit file to define your consensus.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Install Nimbus Consensus Client
Install dependencies.
Build the binary.
Verify Nimbus was built properly by displaying the version.
Install the binary.
Create a service user for the consensus service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Setup ownership permissions.
Create a systemd unit file to define your consensus.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Run the following to quickly sync with Checkpoint Sync.
Install Lodestar Consensus Client
Install dependencies.
Install yarn.
Install nodejs.
Build the binaries.
Verify Lodestar was built properly by displaying the version.
Sample output of a compatible version.
🌟 Lodestar: TypeScript Implementation of the Ethereum Consensus Beacon Chain.
Version: v1.4.1/bff1438
by ChainSafe Systems, 2018-2022
Install the binaries.
Create a service user for the consensus service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Setup ownership permissions.
Create a systemd unit file to define your consensus.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Install Prysm Consensus Client
Install Bazel
Build the binaries.
Verify Prysm was built properly by displaying the help menu.
Install the binaries.
Create a service user for the consensus service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Setup ownership permissions.
Update firewall rules for Prysm, then verify.
Example of firewall status.
Create a systemd unit file to define your consensus.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Run the following to enable auto-start at boot time.
Finally, start your consensus layer client and check it's status.
Press Ctrl + C to exit the status.
Check your logs to confirm that the execution and consensus clients are up and syncing.
Example of Synced Execution Client Logs
Nethermind
A properly functioning Nethermind execution client will indicate "block nnn ... was processed". For example,
Erigon
A properly functioning Erigon execution client will indicate "Handling new payload". For example,
Geth
A properly functioning Geth execution client will indicate "Imported new potential chain segment". For example,
Besu
A properly functioning Besu execution client will indicate "Fork-Choice-Updates". For example,
Known error in Lodestar/Besu consensus logs: As noted in Lodestar's discord, there will be a noisy error about updating eth1 chain cache. This does not seem to affect node syncing or validator duties.
Example error output:
Example of Synced Consensus Client Logs
Lodestar Consensus
A properly functioning Lodestar consensus client will indicate "info: Synced". For example,
Press Ctrl + C to exit the logs.
Since the network is relatively new, syncing both the execution and consensus layers should take less than an hour.
Syncing is complete when your latest block and slot number matches the public block explorers.
Consensus client: check latest slot number with https://zhejiang.beaconcha.in
Execution client: check latest block number with https://blockscout.com/eth/zhejiang-testnet
Step 7. Configure MetaMask and Use the Testnet Faucet
Configure your MetaMask to point to the Zhejiang testnet or use your own node.
Use remote RPC from ethpandaops.io
1) Visit https://zhejiang.ethpandaops.io website
2) Click the "Add Network to MetaMask" button
Use my node
1) Setup SSH tunnel
Note: If your node and where metamask resides is on the same local laptop/desktop/server, skip step 1.
If your node is remote or on another machine, open a SSH tunnel to your node.
For Mac/Linux,
Typically you an open a ssh tunnel with the following:
For Windows using Putty, configure the SSH Tunnel as follows:
1) Navigate toConnection > SSH > Tunnels
2) Set Source port: 8545
3) Set Destination: localhost:8545
4) Click Add button, then Open Button

2) Add a network to Metamask:
Go to Metamask > Settings> Networks > Add a network > Localhost 8545
Configure your Metamask as follows:
Network name: Zhejiang Localhost 8545
New RPC URL: http://localhost:8545
Chain ID: 1337803
Currency symbol: ETH
Block explorer URL: https://blockscout.com/eth/zhejiang-testnet

Use the Testnet faucet to acquire at least 32 Zhejiang testnet ETH for 1 validator. It may take a few moments, sometimes up to an hour, for the funds to appear in your wallet. Or request funds from the ethStaker Discord in the #request-zhejiang-eth channel. Alternatively, use the POW faucet by pk910
For security and privacy reasons, it is best practice to use a brand new unused ETH address for these testnet activities. Avoid re-using any of your existing mainnet ETH addresses.
Step 8. Generate Validator Keys
With two easy methods, your can setup your mnemonic keys with either:
staking-deposit-cli - the original command line based key generator
Staking Deposit CLI Instructions
For the command line method,
Verify the SHA256 Checksum matches the checksum on the releases page.
Example valid output:
staking_deposit-cli-ef89710-linux-amd64.tar.gz: OK
Only proceed if the sha256 check passes with OK!
Extract the archive.
Make a new mnemonic and replace <ETH_ADDRESS_FROM_IDEALLY_HARDWARE_WALLET> with your ethereum withdrawal address, ideally from a Trezor, Ledger or comparable hardware wallet. Adjust number of validators accordingly.
Run the following, in case of this error: RuntimeError: Click will abort further execution because Python 3 was configured to use ASCII as encoding for the environment.
Wagyu Instructions
For the Wagyu key gen app, make sure to select the Zhejiang network and follow the guided steps.
Wagyu (formerly known as StakeHouse) is an application aimed at lowering the technical bar to staking on Ethereum 2.0.
Download Wagyu: https://wagyu.gg
Github: https://github.com/stake-house/wagyu-installer
After creating the validator keys locally, you'll want to copy these validator keys via USB key or rsync file transfer to your staking node.
To align with this guide's steps, first make a default path to store your validator keys
If using USB key, mount the key then copy.
If using rsync, copy your validator keys from your local computer to your staking node with the following command. Change ssh port if needed.
Don't lose your keystore password and write down your 24 word secret mnemonic key! Ideally keep this offline but for testnet purposes it's okay to save digitally for your convenience.
Step 9. Sign up to be a Validator at the Launchpad
After running the staking deposit tool, you will have a deposit_data-##########.json file which you'll upload to the Launchpad.
Your deposit_data file is located in the following location:
Ensure your MetaMask is switched to the Zhejiang Testnet network.
Follow along the instructions at the Launchpad. You'll complete this process when you've uploaded your deposit_data-##########.json file and sent the corresponding 32 Zhejiang testnet ETH deposit to the Zhejiang staking deposit address.
The Zhejiang network staking deposit address is 0x4242424242424242424242424242424242424242
After sending the deposit with Metamask, verify your deposit was completed on a block explorer.
Step 10. Setup Validator Client
Setup Lighthouse Validator
Create a service user for the validator service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Import your validator keys by importing your keystore file. Be sure to enter your keystore password correctly.
Setup ownership permissions, including hardening the access to this directory.
Verify that your keystore file was imported successfully.
Once successful, you will be shown your validator's public key.
For example, 0x8d9138fcf5676e2031dc4eae30a2c92e3306903eeec83ca83f4f851afbd4cb3b33f710e6f4ac516b4598697b30b04302
Monitor your validator's status and performance at https://zhejiang.beaconcha.in by entering your validator's public key.
Create a systemd unit file to define your validator.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
If you wish to customize a graffiti message that is included when you produce a block, add your message between the double quotes after --graffiti.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Setup Teku Validator
Note: Teku combines consensus and validator clients into one binary and service.
First, copy your validator_keys to the data directory.
Storing your keystore password in a text file is required so that Teku can decrypt and load your validators automatically.
Create a file to store your keystore password. Type your password in this file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Confirm that your keystore password is correct.
When specifying directories for your validator-keys, Teku expects to find identically named keystore and password files.
For example keystore-m_12221_3600_1_0_0-11222333.json and keystore-m_12221_3600_1_0_0-11222333.txt
Run the following command to create a corresponding password file for every one of your validators.
Setup ownership permissions, including hardening the access to this directory.
Verify that your validator's keystore .json files and validator's passwords .txt files are present by checking the following directory.
Setup Nimbus Validator
Note: Nimbus combines consensus and validator clients into one binary and service.
The following command will import your validator keys.
Enter your keystore password to import accounts.
Setup ownership permissions, including hardening the access to this directory.
Now you can verify the accounts were imported successfully by doing a directory listing.
You should see a folder named for each of your validator's pubkey.
Setup Lodestar Validator
Create a service user for the validator service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Import your validator keys by importing your keystore file. Be sure to enter your keystore password correctly.
Setup ownership permissions, including hardening the access to this directory.
Verify that your keystore file was imported successfully.
Once successful, you will be shown your validator's public key.
For example, 0x8d9138fcf5676e2031dc4eae30a2c92e3306903eeec83ca83f4f851afbd4cb3b33f710e6f4ac516b4598697b30b04302
Monitor your validator's status and performance at https://zhejiang.beaconcha.in by entering your validator's public key.
Create a systemd unit file to define your validator.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
If you wish to customize a graffiti message that is included when you produce a block, add your message between the double quotes after --graffiti.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Setup Prysm Validator
Create a service user for the validator service, as this improves security, then create data directories.
Storing your keystore password in a text file is required so that Prysm can decrypt and load your validators automatically.
Create a file to store your keystore password. Type your password in this file.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Confirm that your keystore password is correct.
Import your validator keys by importing your keystore file. Be sure to enter your keystore password correctly.
Setup ownership permissions, including hardening the access to this directory.
Verify that your keystore file was imported successfully.
Once successful, you will be shown your validator's public key. For example:
Monitor your validator's status and performance at https://zhejiang.beaconcha.in by entering your validator's public key.
Create a systemd unit file to define your validator.service configuration.
Paste the following configuration into the file. Replace <enter-eth-address-here> with your suggested fee recipient ETH address.
If you wish to customize a graffiti message that is included when you produce a block, add your message between the double quotes after --graffiti.
To exit and save, press Ctrl + X, then Y, then Enter.
Run the following to enable auto-start at boot time.
Finally, start your validator client and check it's status.
Check your logs to confirm that the validator clients are up and functioning.
Example of Synced Validator Client Logs
Lodestar Validator
A properly functioning Lodestar validator will indicate publishing of attestations. For example,
Press Ctrl + C to exit the logs.
After making your 32 ETH deposit, your validator is placed into queue for activation which typically takes 6-24 hours. Once activated, your validator begins staking and attestation duties. Learn more about the depositing process.
🎉Congrats on setting up your Zhejiang “Withdrawals” staking node!
Step 11. Next Steps
As a newly minted Zhejiang Ethereum Staker,
Learn more about what features are introduced and being tested on Zhejiang.
Monitor your validator's earnings and performance at https://zhejiang.beaconcha.in by entering your validator's public key.
Learn to connect your MetaMask wallet to your own execution layer node. See step 7, use my own node.
Additional Commands
Extra Testing Commands
Perform a Voluntary Exit
Stop Lodestar validator
Run the voluntary exit command and follow the instructions
Restart validator
Your Github Contributions Welcome
This guide is fully open source and fully powered by home stakers like you. 🙏
Pull requests or issues can be submitted on github:
Support Us
These guides are solely supported by Gitcoin Grants and donations to our Cointr.ee by stakers like you. 🙏
Marvelous Reference Material
Technical Support and Community
Reddit > https://www.reddit.com/r/ethstaker
Discord > ethStaker > #zhejiang channel
Last Words
I stand upon the shoulders of giants and as such, invite you to stand upon mine. Use my work with or without attribution; I make no claim of "intellectual property." My ideas are the result of countless millenia of evolution - they belong to humanity.