Step 4: Installing consensus client
Your choice of either Lighthouse, Lodestar, Teku, Nimbus, or Prysm.
Only one consensus client is required per node.
Consensus Client Diversity
To strengthen Ethereum's resilience against potential attacks or consensus bugs, it's best practice to run a minority client in order to increase client diversity.
Find the latest distribution of consensus clients here: https://clientdiversity.org
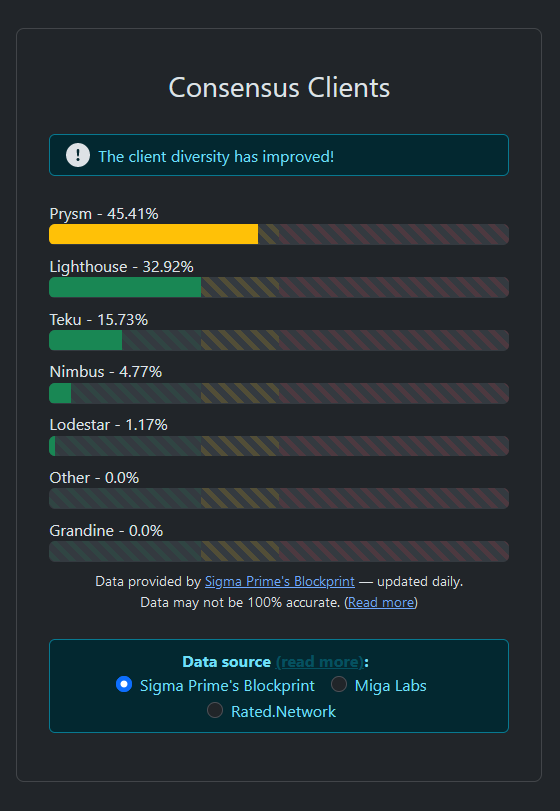
Overview of Consensus Clients
🛡️ Recommendation 🛡️: Teku, Nimbus, or Lodestar
Lighthouse
Lighthouse: Open-source Ethereum 2.0 project by Sigma Prime, following Ethereum Foundation Research specification.
Innovative features: Implements advanced blockchain technologies like proof-of-stake consensus, parallel transaction execution, and sharding (state separation).
Independently managed: Not officially affiliated with the Ethereum Foundation, adheres to their guidance as long beneficial for Ethereum protocol and community.
Implemented in Rust: Prioritizes security and efficiency through language choice.
Lodestar
Lodestar: Open-source Ethereum consensus client by ChainSafe Systems, known for production-ready beacon chain and validator client.
Flagship product: Ideal for researchers and developers due to rapid prototyping and browser usage capabilities.
Typescript implementation: Distinctive feature, aligns with familiarity of millions of developers worldwide.
Light client expertise: Pioneering research, standardization, and implementation of Ethereum light clients.
Collaborative approach: Works with other implementers, researchers, and developers to promote trustless data usage from the blockchain.
Teku
Teku (formerly Artemis): Enterprise-focused Ethereum consensus client developed by PegaSys, an ConsenSys division.
Apache 2.0 licensed: Open-source with flexible usage permissions.
Written in Java: Mature and widely used programming language for increased institutional appeal and security requirements.
Developed by PegaSys: An arm of ConsenSys dedicated to creating enterprise-ready Ethereum clients and tools.
Nimbus
Nimbus: Open-source Ethereum client compatible with both Ethereum 2.0 and Ethereum 1.0.
Lightweight resource usage: Designed for optimal performance on embedded systems and resource-restricted devices.
Versatile application: Also suitable for running alongside other workloads, beneficial for stakers looking to minimize server costs.
Implemented in Nim: Written using the Nim programming language.
Maintained by Status.im team.
Prysm
Prysm: Full-featured Ethereum 2.0 implementation in Go programming language.
Developed by Prysmatic Labs.
Adheres to official Ethereum 2.0 specification, evolving collectively through research and development efforts from various Ethereum ecosystem teams including the Ethereum Foundation.
Comparison of Consensus Clients
Lighthouse
Medium
6 GB
120 - 150 GB
Instant via checkpoint
Lodestar
Medium
8 GB
120 - 150 GB
Instant via checkpoint
Teku
Medium
10 GB
120 - 150 GB
Instant via checkpoint
Nimbus
Low
3 GB
120 - 150 GB
Instant via checkpoint
Prysm
Medium
6 GB
120 - 150 GB
Instant via checkpoint
Notes:
As databases expand beyond 300GB in size over time, checkpoint sync allows nodes to efficiently resynchronize and significantly reduce their database sizes while minimizing downtime.