Configuring Slot Leader Calculations
🔥 Hot tip: You can calculate your slot leader schedule, which tells you when it's your stake pools turn to mint a block. This can help you know what time is best to schedule maintenance on your stake pool. It can also help verify your pool is minting blocks correctly when it is your pool's turn. This is to be setup and run on the block producer node.
Since version 1.34, it is possible to check the slot leadership schedule for the current and next epoch using cardano-cli.
Next epoch's leadership schedule becomes available 1.5 days (36 hours) before the end of the current epoch.
Next epoch's leadership schedule is obtained with the following:
cardano-cli query leadership-schedule \
--mainnet \
--genesis $NODE_HOME/shelley-genesis.json \
--stake-pool-id $(cat $NODE_HOME/stakepoolid.txt) \
--vrf-signing-key-file $NODE_HOME/vrf.skey \
--nextCurrent epoch's leadership schedule is obtained with the following:
cardano-cli query leadership-schedule \
--mainnet \
--genesis $NODE_HOME/shelley-genesis.json \
--stake-pool-id $(cat $NODE_HOME/stakepoolid.txt) \
--vrf-signing-key-file $NODE_HOME/vrf.skey \
--currentExample leadership schedule output:
SlotNo UTC Time
-------------------------------------------------------------
4073 2021-12-29 17:26:54.998001755 UTC
4126 2021-12-29 17:27:00.298001755 UTC
4206 2021-12-29 17:27:08.298001755 UTC
4256 2021-12-29 17:27:13.298001755 UTC
4309 2021-12-29 17:27:18.598001755 UTC
4376 2021-12-29 17:27:25.298001755 UTC
4423 2021-12-29 17:27:29.998001755 UTC
4433 2021-12-29 17:27:30.998001755 UTC🔁 Automate the process with Cronjob:
The automation of this process will work with the following method, as said, next epoch blocks can be checked 1.5 days before the start of the next epoch or at the 75% of the current epoch's completion. What the script will do, is to calculate the correct day and hour to run the command, then wait until it is possible to do that and once the selected time comes, run the check listed below. Once finished, it will redirect the output into a log file that can be analyzed.
Keep in mind that running the leadership-schedule command, listed below and used by the script, with the cardano-node at the same time, will use approximately 17GB of RAM at the time of writing this guide (April 2022).
The possible solutions to avoid a node crash are:
Increase the RAM of the node
Credits to Techs2help for developing the script.
Create the leaderScheduleCheck.sh script file in the block producer (script can also be run on a relay node but vrf.skey needs to be exported there) and paste the following code inside of it:
Set the following variables with your data:
Add execution permissions and test that the script is running without errors:
If everything is working correctly, an output as the follow will be presented:
Current epoch: 199 Epoch start time: 04/14/22 20:20:16 Epoch end time: 04/19/22 20:10:16 Current cron execution time: 04/18/22 15:37:51 Next check time: 04/18/22 14:12:46 [...] Cutted output cause it can vary based on time when the script is ran
Configure Cronjob to make the script run automatically:
To configure the job at the start of an epoch, keep in mind the following information:
Epoch in MAINNET starts at 21:45 UTC
Find the time when the cronjob should start:
Cronjobs run based on local timezone, not on UTC hours. \
Find timezone:
timedatectl | grep "Time zone"
Once you found your timezone, you need to understand when run the job (It isn't mandatory to run it at epoch's starting hour). Here is an example with a UTC+2 timezone for Mainnet:
Epoch starting hour UTC: 21:45 Epoch starting hour for requested timezone: 23:45 Cronjob will be set to run at 23:45
Add cronjob and edit parameters based on your needs, PATH, NODE_HOME, NODE_CONFIG, CARDANO_NODE_SOCKET_PATH, MM, HH, path_to_script and desired_log_folder:
Once the cronjob is set, the script will be run every day and it will check if in the next 24H, it will be the correct time to run the command and see if there are scheduled blocks in the next epoch. For every epoch, there will be a file called leaderSchedule_epoch.txt
🧬 Installing the Binary
Confirming That CNCLI is Properly Installed
Run the following command to check if cncli is correctly installed and available in your system PATH variable:
It should return /usr/local/bin/cncli
⛏️ Running LeaderLog with stake-snapshot
This command calculates a stake pool's expected slot list.
prevandcurrentlogs are available as long as you have a synchronized database.nextlogs are only available 1.5 days (36 hours) before the end of the epoch.You need to use
poolStakeMarkandactiveStakeMarkfornext,poolStakeSetandactiveStakeSetforcurrent,poolStakeGoandactiveStakeGoforprev.
Example usage with the stake-snapshot approach for next epoch:
Run this command 1.5 days (36 hours) before the next epoch begins.
Example usage with the stake-snapshot approach for current epoch:
Example usage with the stake-snapshot approach for previous epoch:
Integrating with PoolTool
PoolTool provides example scripts to submit the following data for your stake pool:
Current block height
The number of slots in which your stake pool is currently elected to mint blocks
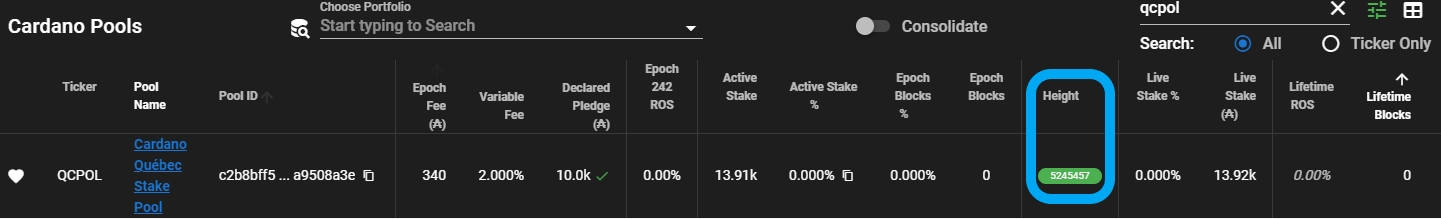
The following figure shows the green badge that PoolTool displays next to your stake pool when your node is fully synchronized with the blockchain (image credit to QCPOL):
You can also use CNCLI utilities developed by the Cardano Community to send the block height and slot count to PoolTool.
Guild Operators maintain the cncli.sh companion script to help stake pool operators use the Cardano Community's CNCLI utilities.
To send data to PoolTool using CNCLI utilities without using the cncli.sh script, create a configuration file containing your PoolTool API key and stake pool details.
For details on requesting an API key from PoolTool, see the topic Obtaining a PoolTool API Key.
To create a configuration file, update values in the following example with your pool information. To follow the example, save the configuration file at $NODE_HOME/scripts/pooltool.json
Creating systemd Services
CNCLI sync and sendtip can be easily enabled as systemd services. When enabled as systemd services:
syncwill continuously keep thecncli.dbdatabase synchronized.sendtipwill continuously send your stake pooltipto PoolTool.
To set up systemd:
Create the following and move to
/etc/systemd/system/cncli-sync.service
Create the following and move to
/etc/systemd/system/cncli-sendtip.service
To enable and run the above services, run:
🛠️ Upgrading CNCLI
Confirming CNCLI Upgrades
It should return the updated version number.
Credits for inventing this process goes to the hard work by Andrew Westberg @amw7 (developer of JorManager and operator of BCSH family of stake pools).
Check if you have python installed.
Otherwise, install python3.
Check if you have pip installed.
Install pip3 if needed.
Install pytz which handles timezones.
Verify python and pip are setup correctly before continuing.
Clone the leaderLog scripts from papacarp/pooltool.io git repo.
Official documentation for this LeaderLogs tool can be read here.
Calculate your slot leader schedule for the latest current epoch.
Set the timezone name to format the schedule's times properly. Use the --tz option. [Default: America/Los_Angeles]') Refer to the official documentation for more info.
🤖 Pro Tip: 1.5 days before the end of the current epoch, you can find the next epoch's schedule.
🤖 Pro Tip #2: Add the flag --epoch <INTEGER #> to find a specific epoch's slot schedule.
🤖 Pro Tip #3: Ensure your slot leader scripts are up to date.
If your pool is scheduled to mint blocks, you should hopefully see output similar to this. Listed by date and time, this is your slot leader schedule or in other words, when your pool is eligible to mint a block.
Your slot leader log should remain confidential. If you share this information publicly, an attacker could use this information to attack your stake pool.